Record Testing help tester to record & run their activity against test target. It is a type of automated testing but for multiple users. This tutorial guides you how to use Proxy Server to record your test.
The Proxy Server allows JMeter to watch and record user activity while they are browsing web application with a normal browser.
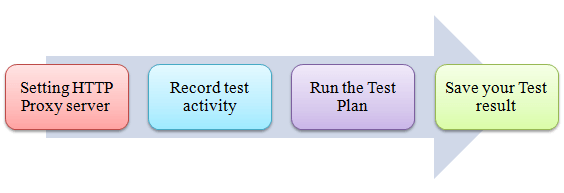
In this tutorial, you will learn
- Step 1) Setting HTTP Proxy server
- Step 2) Record your activity
- Step 3) Run your Test Plan
- Step 4) Save your test result
Here is the roadmap of this practical example
Step 1) Setting the HTTP Proxy server
This is a Step-by-step guide to setup proxy
- Start JMeter
- Select Test Plan on the tree
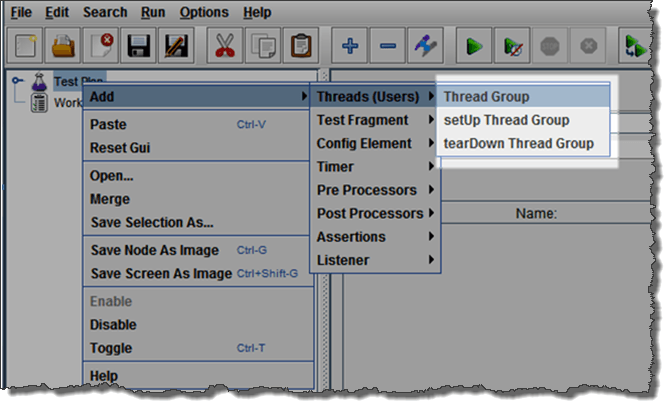
- Add Thread GroupRight click on the Test Plan and add a new thread group: Add => Threads (Users) =>Thread Group
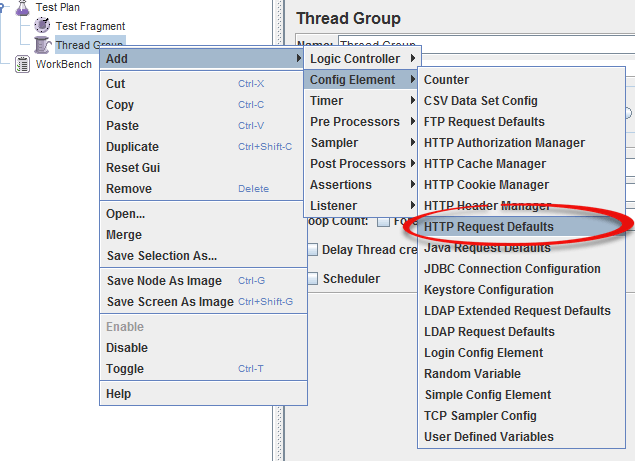
- Add HTTP RequestSelect the Thread Group; right click Add => Config Element => HTTP Request Defaults
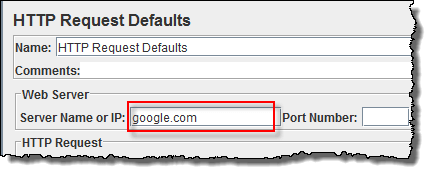
In new HTTP Request Defaults element: In Server name or IP, enter "google.com". You should keep the others fields blank
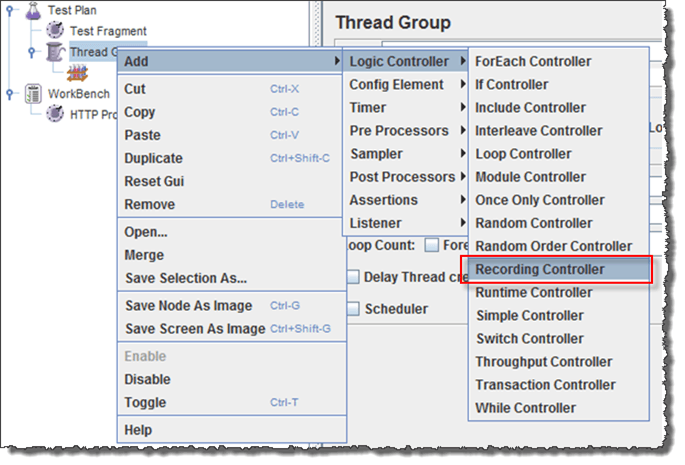
- Add Recording ControllerRight click on the "Thread Group" and add a recording controller: Add => Logic Controller =>Recording Controller
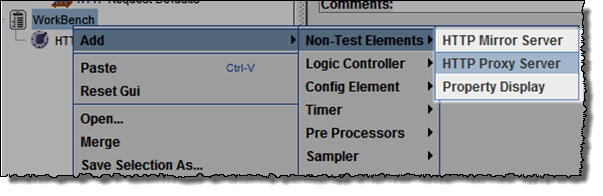
- Add Proxy Server to WorkBenchRight click on the Workbench and add the http proxy: Add => Non-Test Elements => HTTP Proxy Server
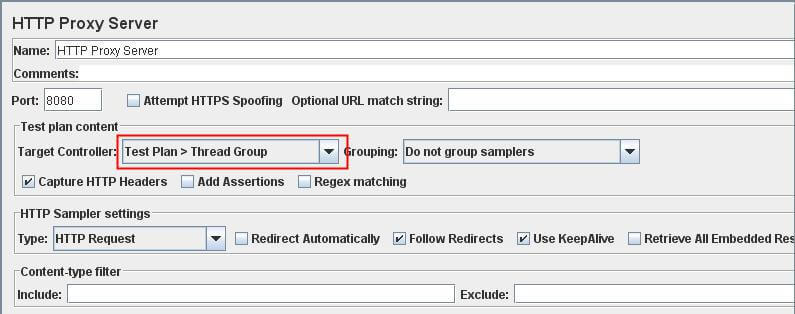
- Set Target Controller where your recorded scripts will be added
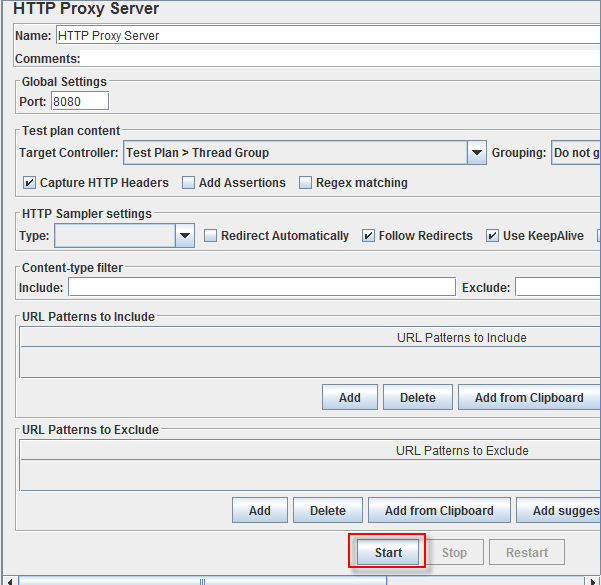
- Start Proxy ServerReturn to HTTP Proxy Server, and click the Start button at the bottom. Now your JMeter proxy server start
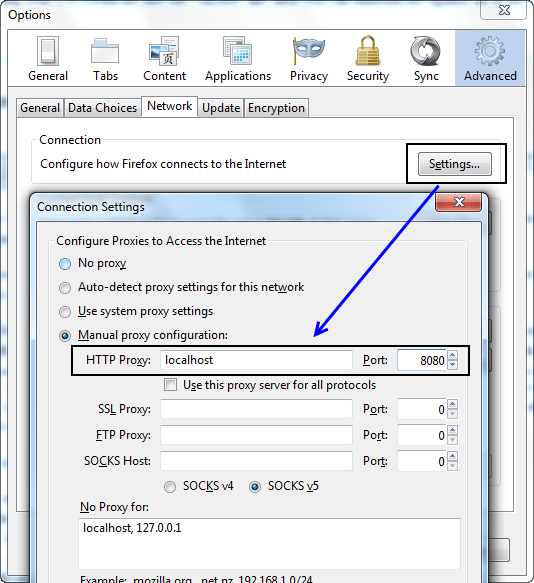
- Start your Browser choose Tool => Option => Advanced => Network => Setting => Enter HTTP proxy as figure below
Step 2) Record your activity
- Now Launch http://www.google.com in your web browser (JMeter still open)
- Do activities search the keyword "apache".
- Back to JMeter, in HTTP Proxy Server, click Stop when finished
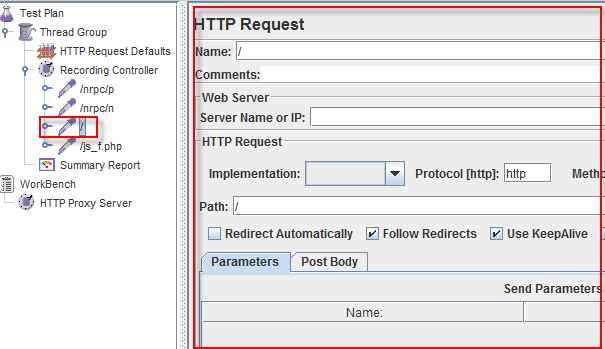
- After finishing recording, you will see JMeter automatically created a new HTTP request as the figure belowJMeter has already recorded a user request to the Home Page of Google website. Http://www.google.com/The other HTTP requests display in above figure, you should remove them. Because sometime JMeter also records some advertising links while you are searching keyword on Google. We should ignore them in our Test Plan
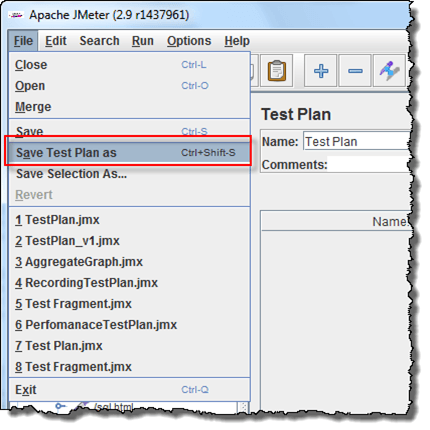
- Click File => Save your Test Plan as
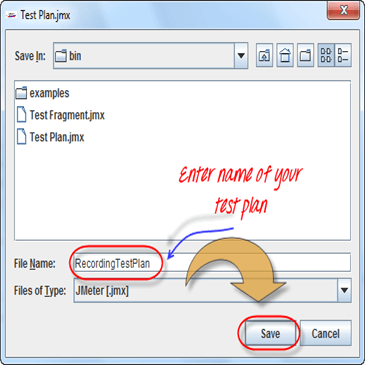
- A Dialog box display => enter a name of your test plan at File Name field => Click SaveNow your Test Plan is saved under name RecordingTestPlan.jmx
Step 3) Run your Test Plan
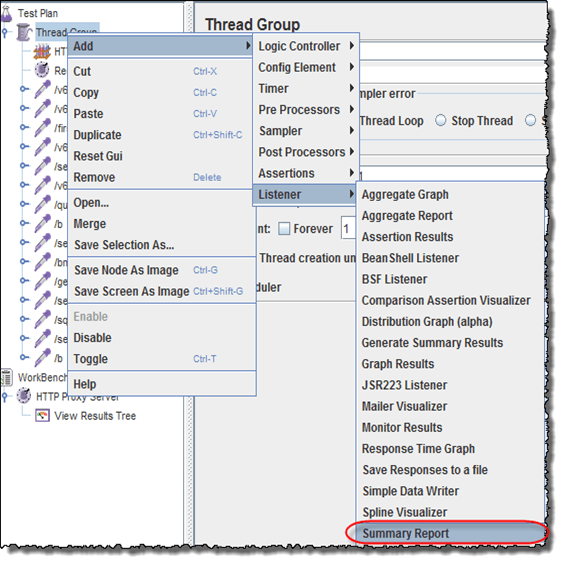
- Select Thread Group => Add => Listener=> Summary Report
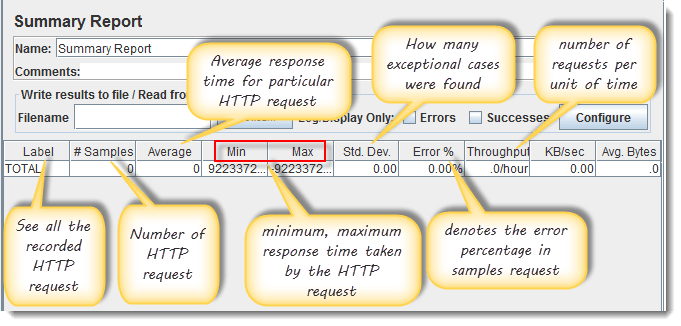
- The Summary Report will show some basic statics
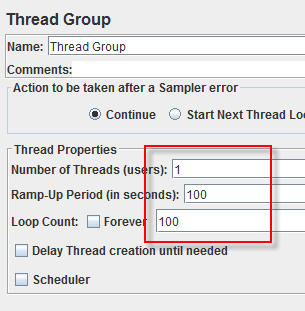
- Select Thread Group, enter information as the figure below
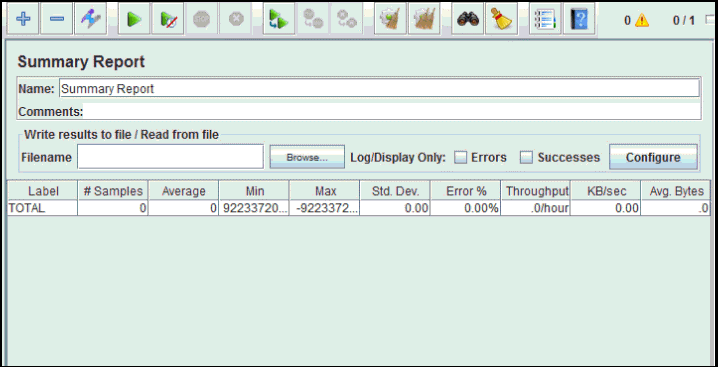
- Before you start the test, select "Summary Report". When you ready to run a test, select Run => Start (Ctrl+R). JMeter will playback your activity in 100 timesAs the test runs, the statistics will change until the test is done.
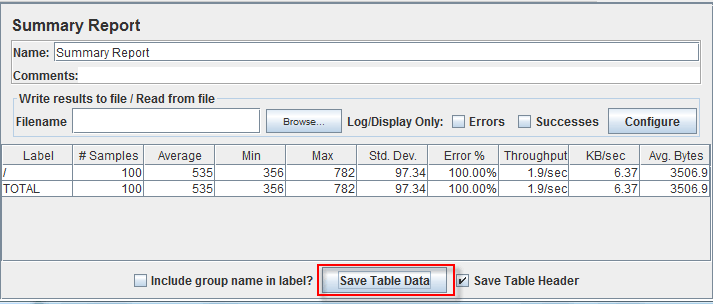
Step 4) Save your test result
- Click Save Table Data to save test result to file
- Enter the name of the test result and click Save. Test Result in JMeter is saved in *.csv format as default

.png)
.png)


